Hubei Aier Eye Hospital Successfully Performs Third-Generation FCVB Surgery, Preserving Eyeball for Severe Ocular Trauma
Release time: Aug 13,2025
Hubei Aier Eye Hospital successfully performed the first third-generation Foldable Capsular Vitreous Body (FCVB) surgery in the hospital. Professor Wang Guohua's team implanted the third-generation FCVB for a patient with silicone oil-dependent eye, preserving hope. As a new eye-preserving technology, FCVB provides a new treatment method for patients with fundus diseases such as severe retinal detachment, ocular trauma, and silicone oil-dependent eye, and is of great significance in saving patients' eyeballs.
Condition Overview
The patient is a 26-year-old male. He underwent femtosecond laser myopia surgery in 2017. Three weeks ago, after a traffic accident, he experienced decreased vision, bleeding, and eye pain in his right eye. He was diagnosed with a ruptured right eyeball in another hospital and received emergency suture surgery for the right facial wound and the ruptured eyeball. Due to the severe injury and persistent eye discomfort, the patient and his family came to Hubei Aier Eye Hospital hoping for further treatment.
Professor Wang's team examined him: the right eye had no light perception in the naked eye; the intraocular pressure of the right eye was 3 mmHg (measured by NCT); the right eyeball showed mild enophthalmos with limited upward movement, mild displacement of the central corneal flap, stromal edema around the corneal flap, and the rest of the cornea was transparent; the anterior chamber was deep; no iris tissue was found in the pupil area; there was circumferential ciliary process eversion; the ciliary body was adherent to the white proliferative membrane in the pupil area; the pupil area was covered by white proliferative membrane and hemorrhage, making it impossible to see clearly beyond.
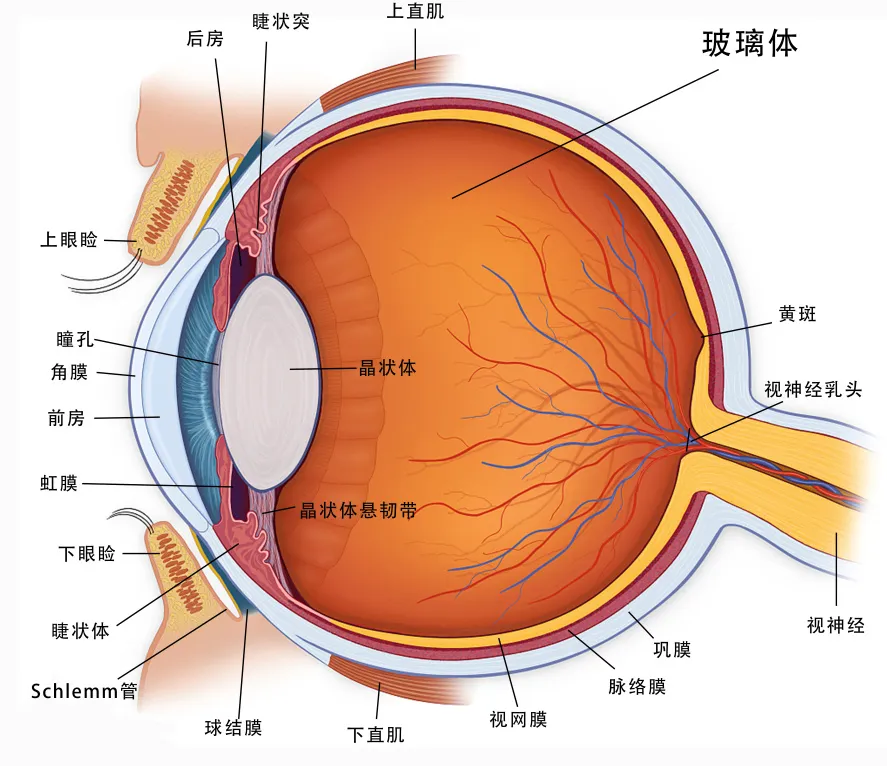
Given the severe injury, the patient's eyeball showed a tendency to atrophy, requiring immediate eye-preserving surgery. Otherwise, severe atrophy would risk eyeball removal. After detailed examinations, comparison of multiple treatment plans, and full communication with the patient, Professor Wang's team decided to perform the third-generation Foldable Capsular Vitreous Body (FCVB) implantation.
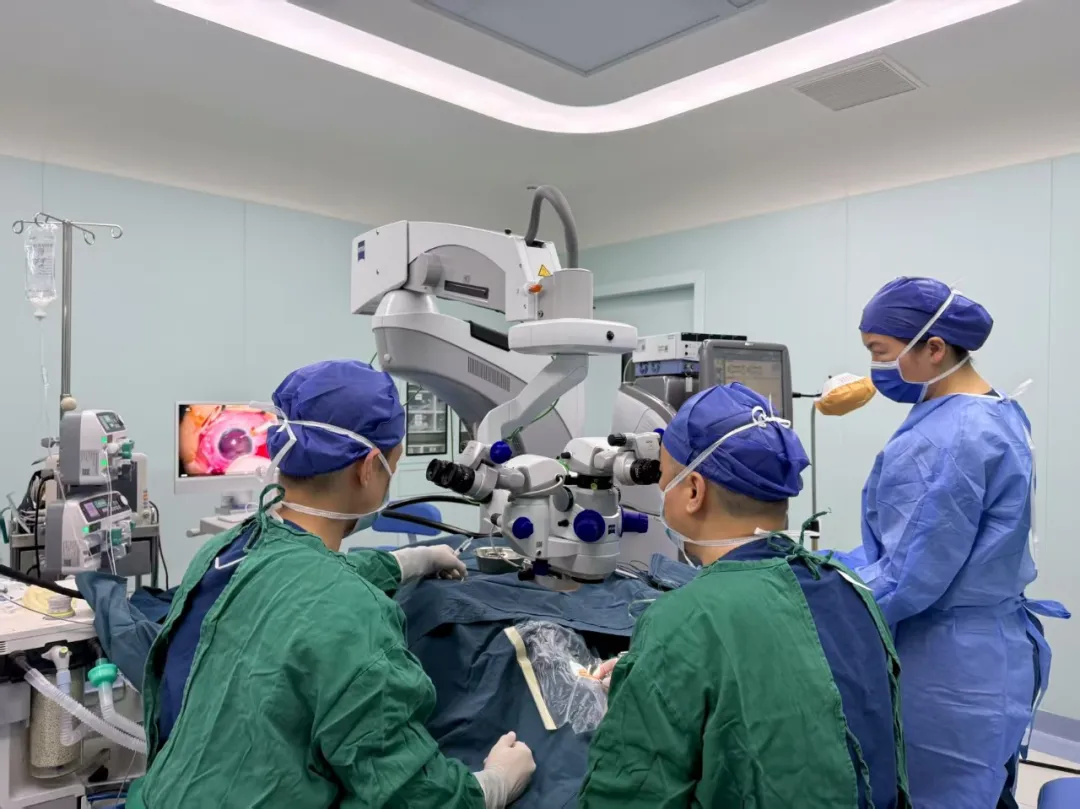
On August 7th, Professor Wang's team performed the third-generation FCVB surgery on the patient. The folded FCVB was implanted into the eye through a minimally invasive incision, and silicone oil was injected into the FCVB via the drainage valve to support the retina and maintain intraocular pressure. Finally, the third-generation FCVB was successfully implanted into the patient's eye. Postoperative review showed that the FCVB in the right eye was in the correct position, the intraocular pressure was 15 mmHg, and the anterior chamber was deep. The patient was satisfied with the postoperative effect and expressed sincere gratitude to the doctors!
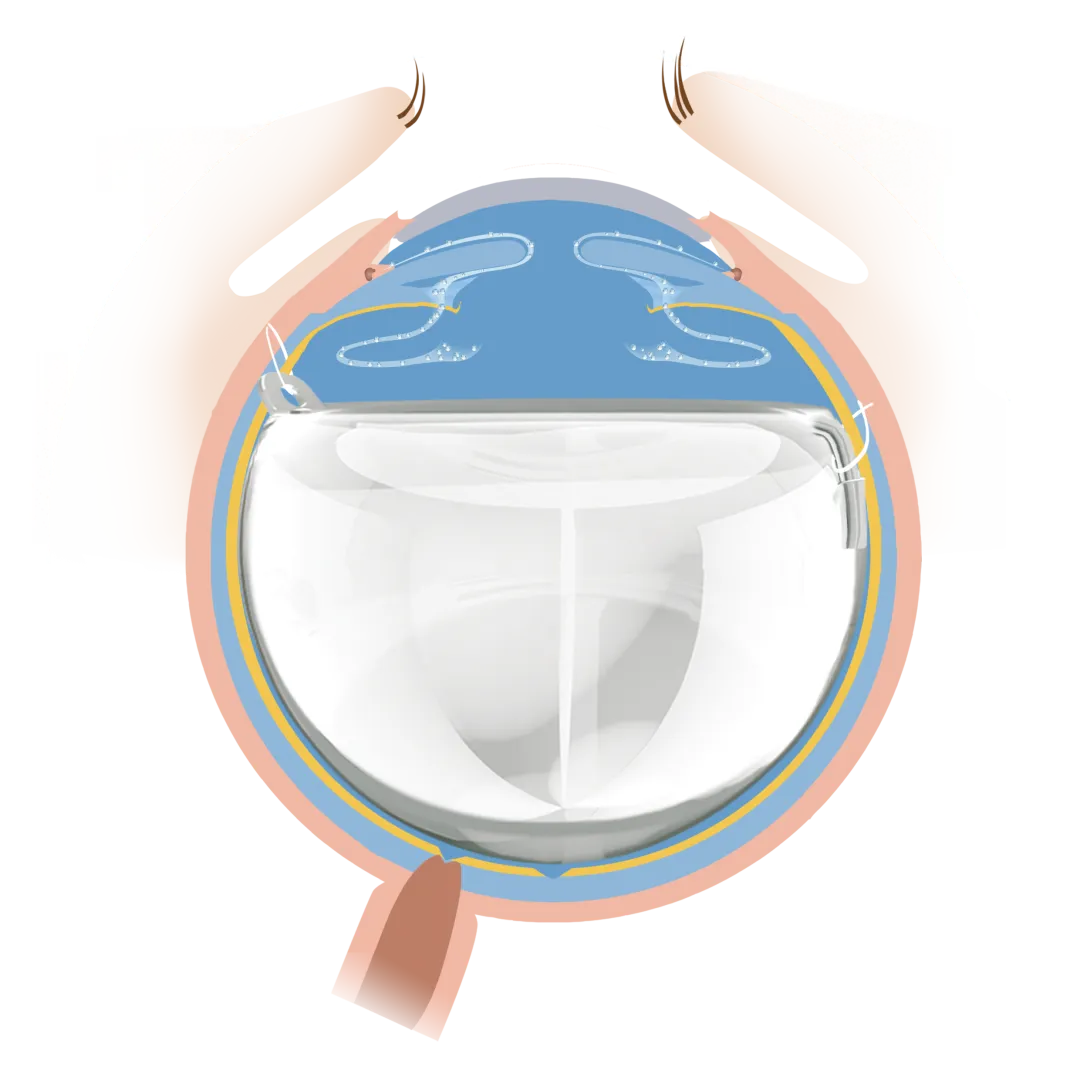
Professor Wang introduced that FCVB is the first international innovative product simulating the human natural vitreous body. It consists of a capsular body, a drainage tube, a drainage valve, and a fixation loop. The capsular body is precisely simulated based on the parameters of the human vitreous cavity through computer technology, with a special planar design for the lens surface. Its raw material is imported medical silicone polymer approved by the US FDA. During the surgery, the FCVB is folded and implanted into the vitreous cavity, and silicone oil is injected through the drainage valve. The FCVB is fixed in the eye through double loops (fixation loop and suture on the drainage tube), isolating the ciliary body from damage caused by silicone oil.
The FCVB can preserve the posterior chamber space, allowing the ciliary body to slowly recover its function, saving the dysfunctional ciliary body and maintaining intraocular pressure; it avoids silicone oil emulsification and displacement; and comprehensively supports the retina and maintains the eyeball shape.
Doctor's Profile

Professor Wang Guohua
Chief Physician
Master's Supervisor
Academic Positions: Standing Committee Member of the 4th Ophthalmologists Branch of Hubei Provincial Medical Doctor Association; Member of the Fundus Disease Group of Ophthalmology Branch of Hubei Provincial Medical Association; Member of the Fundus Disease Group of Aier Eye Hospital Group; Deputy Leader of the Cataract Group of Hubei Region, Aier Eye Hospital Group.
Position: Director of Fundus Disease Department, Surgeon of Fundus Disease Department.
Profile: Engaged in clinical ophthalmology for 25 years, proficient in the diagnosis and treatment of various fundus diseases, especially with rich and mature experience in the diagnosis and treatment of vitreoretinal diseases, macular diseases, optic nerve diseases, uveitis, etc. Participated in compiling 1 ophthalmology monograph, published nearly 20 papers in domestic and foreign journals (including 2 SCI-indexed papers), and presided over or participated in multiple provincial and municipal scientific research projects.
Specializes in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of complex retinal detachment, complex ocular trauma, retinal angiomatosis, retinal vasculitis, diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and vitreous diseases.
Hospital Introduction

Wuhan University Affiliated Aier Eye Hospital (Wuhan Aier Eye Hospital) is a large tertiary specialized eye hospital approved by Hubei Provincial Health Commission in 2003, integrating medical treatment, teaching, scientific research, myopia prevention and control, and blindness prevention and treatment. The hospital has been successively recognized as a National Drug Clinical Trial Institution and a Standardized Training Base for Resident Physicians in Ophthalmology; in 2016, it was identified as a Clinical Key Specialty (Ophthalmology) of Hubei Provincial Tertiary Hospitals and a Municipal Clinical Key Specialty (Ophthalmology) of Wuhan; it has won honors such as the "May 1st Labor Medal" of Wuhan. In the 2019 China Hospital Science and Technology Value (STEM) ranking in ophthalmology, it ranked 50th in the country.
Wuhan Aier Eye Hospital (Wuhan University Affiliated Aier Eye Hospital) has set up Wuhan University Aier Ophthalmology Clinical College, Wuhan University Aier Ophthalmology Research Institute, Wuhan Aier Ophthalmology Research Institute, and Wuhan Aier Eye Bank. It has 632 hospital beds. There are 846 medical and health personnel, including 33 chief physicians, 79 associate chief physicians, and 154 attending physicians. There are 75 optometrists, including 19 national first-class (senior) optometrists and 20 national second-class optometrists. There are 35 master's and doctoral supervisors, 60 doctors, and 190 masters. A total of 49 experts hold academic positions in national, provincial, and municipal ophthalmological academic organizations. 15 doctors have been selected as young and middle-aged medical backbone talents in Wuhan.
In the past decade, the hospital has undertaken 2 projects of Hubei Provincial Department of Science and Technology, 25 projects of Hunan Provincial Department of Science and Technology, 12 projects of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, and 63 projects of Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. It has produced 124 patents for scientific research achievements, 13 software copyrights, and more than 349 scientific papers (including more than 72 SCI journal papers). In 2008, as the editor-in-chief, it founded the medical journal Ophthalmic Practice and Research, which has published 55 issues so far; 13 medical monographs have been compiled and published. It has hosted 10 national medical continuing education programs, 20 provincial continuing education programs, and 10 municipal continuing education programs.
The hospital is committed to introducing internationally advanced ophthalmic technologies, adopting modern management concepts and medical management concepts, adhering to the path of specialization, standardization, and intelligent development, and promoting the high-quality development of ophthalmic medical care in Hubei Province and even the whole country.
The surgery not only averted the risk of eyeball atrophy but also preserved his precious visual function.
12/30
Two days later, laser photocoagulation was performed on the retinal hole in the right eye. Postoperative examination showed the retinal hole was located on the buckle ridge with good adhesion. The patient and her family were satisfied with the postoperative outcome and expressed their gratitude to Director Li's team!
12/24







